Functions Reference
This reference lists all the Functions under Tools > Functions on the Mapping page that are available for use when editing field definitions.
While there is no solid datatype concept, some functions do expect specific "types" (for example, @NUM expects a number or mathematical expression). There are also some special tokens for editing field definitions.
All functions are preceded by the "@" symbol.
@ABS(Value)
Value: Token or hard-coded value.
The "absolute" function or @ABS simply acts like finding the absolute in mathematics, by taking the token or value and converting it into a positive number.
Example: @ABS([T:ITEM_QUANTITY])
Where @ABS(-100) would return 100.
@CASE(Value,DefaultTranslation,CompareValue1,TranslationValue1,...)
Value: Token or hardcoded value.
DefaulTranslation: Value/result to use if no match is found (fallback value)
CompareValue1: Comparison value/token against Value variable
TranslationValue1: Return value/token if CompareValue1 equals true
@CASE allows logic that will look at a single token and compare it against multiple values in which will return the most appropriate result based on that comparison. Only a single return will result at any given time
@COPY(String,StartPos,CopyLength)
String: Token or hard-coded value to alter
StartPos: Position within the Token to start at
CopyLength: Number of characters to copy
@COPY takes a given value, and will return a new value based on where and how many characters you wish to copy, such as producing only part of a value or to cap the length of a value. This also very useful in basing logic specifically on a value in a token.
Example: @COPY([T:STORE_NUMBER],9,4)
Where 9 is the starting position value for the store number, and 4 will be the returning value of the statement. Therefore, if the store number is 0078742030982, then the return value would be 0982.
@DATEADD(Date,DaysToAdd,SkipWeekends)
Date: Token/date value to modify
DaysToAdd: How many +/- days to add/subtract from Date Token
SkipWeekends: 1 to skip weekends. 0 (or omit) to indicate weekends are not skipped
@DATEADD modifies a given date by adding or subtracting days to it, with the option to skip weekends. See Using @DATEDD for various usage examples.
@ERROR(String)
Returns a string message when set up for custom error logic. Used primarily for flat files but can be utilized for frameworking integrations as well. There is a 250 character limit on the message.
Example 1: @IF_THEN_ELSE([T:DATE_PURCHASE_ORDER],<>,,[T:DATE_PURCHASE_ORDER],@ERROR(Purchase Order Date was not provided for PO# [T:PURCHASE_ORDER_NUMBER]))
Example 2 @IF_THEN_ELSE(@NUM([T:ITEM_QUANTITY]),>,@NUM(0),[T:ITEM_QUANTITY],@ERROR(Item Quantity must be greater than 0 for [T:ITEM_UPC]))
@IF_THEN_ELSE(Value1,CompareType,Value2,ValueIfTrue,ValueIfFalse)
Value1: First Value/Token to compare
CompareType: Comparison Operator
Value2: Second Value/Token to compare
ValueIfTrue: Result to return if Value1 compares to Value2 based on CompareType
ValueIfFalse: Result to return if comparison of Value 1 and Value 2 failed
@IF_THEN_ELSE evaluates a comparison of values. If the statement is true, then it will return the value that is set for true, else it will perform the function set for if the first statement is not true..
Comparison operators include <, >, =, <>, <=, >=. Note that the comma represents the ELSE function. If you want to return nothing, add a second comma after the first one.
Example: @IF_THEN_ELSE([I: Account ID],=,ACE,[T:DISTRIBUTOR_ADDRESS_CODE],[T:STORE_NUMBER])
If the trading partner is ACE, then this returns the value of the DC code, else (the trading partner is not 'ACE') this returns the store number. If you wanted to return nothing (instead of the store number) you would use 'ACE,,' in the statement instead.
@IF_AND_THEN_ELSE(Value1,CompareType,Value2,Value3,CompareType,Value4, ... ValueIfTrue,ValueIfFalse)
Value1, Value2, Value3 ... : Values/Tokens to compare
CompareType: Comparison Operator
ValueIfTrue: Result to return if Value1 compares to Value2 based on CompareType
ValueIfFalse: Result to return if comparison of Value 1 and Value 2 failed
@IF_AND_THEN_ELSE evaluates multiple sets of comparisons to return true before returning the true value.
Comparison operators include <, >, =, <>, <=, >=. Note that the comma represents the ELSE function. If you want to return nothing, add a second comma after the first one.
Example: @IF_AND_THEN_ELSE([I: AccountID],=,ACE,([T:TRANSACTION_TYPE_CODE],=,SO,[T:DISTRIBUTOR_ADDRESS_CODE],[T:STORE_NUMBER])
Where if both the trading partner is ACE and the transaction code type is SO, then this will return the value of the DC code, or else it will return the store number.
@IF_OR_THEN_ELSE(Value1,CompareType,Value2,Value3,CompareType,Value4, ... ValueIfTrue,ValueIfFalse)
Value1, Value2, Value3 ... : Values/Tokens to compare
CompareType: Comparison Operator
ValueIfTrue: Result to return if Value1 compares to Value2 based on CompareType
ValueIfFalse: Result to return if comparison of Value 1 and Value 2 failed
@IF_OR_THEN_ELSE allows any condition to evaluate as true in order to return the true value. That is if either statement is true then it will return the ValueIfTrue that is set, else it will return the ValueIfFalse.
Comparison operators include <, >, =, <>, <=, >=. Note that the comma represents the ELSE function. If you want to return nothing, add a second comma after the first one.
Example: @IF_OR_THEN_ELSE([I: Account ID],=,ACE, ([I: Account ID],=,ACE2,[T:DISTRIBUTOR_ADDRESS_CODE],[T:STORE_NUMBER])
If the trading partner is ACE or ACE2, then this will return the value of the DC code, or else it will return the store number.
@INT(Value,Shift,Size)
@INT turns a value into an Integer, placing “0” for shift and/or size if not needed.
Example:@INT([T:ITEM_QUANTITY],0,5)
If item quantity is 1, then the returned value would be 00001.
@INSTR(String,Substring)
String: Token or hard-coded value to search against
Substring: Character/word to look for within the string
@INSTR finds the starting position of the specified character or word.
Example: @INSTR([R:4.10 Item.UserField1],Tracking #)
This returns the position count where 'Tracking #' first appears in the field. That would be the position count of the 'T' in 'Tracking #'. See also Using @INSTR to Parse Data for more usage examples.
@IS_NUMERIC(Value)
Value: Token or hard-coded value.
@IS_NUMERIC returns 1 if value is fully numeric or 0 if it contains string-based characters.
@LEN(String)
@LEN returns how many characters make up a string.
Example: @LEN([T:ITEM_QUANTITY])
Where @LEN(100) would return a value of 3.
@LOWER_CASE (String)
@LOWER_CASE converts any upper-cased characters to lower case.
Example: @LOWER CASE([T:SHIP_TO_NAME])
@NUM(Calculation)
Calculation: Combination of token or hard-coded value.
@NUM serves as a wrapper for performing calculations within a field. Operators include +, -, *, / .
-
Should not have spaces between tokens and operator
-
Only a single math-operation within @NUM statement
-
Nesting @NUM statements to perform multiple calculations
See Using @NUM for usage examples.
@NUM(@SUM(@NUM()))
@NUM(@SUM(@NUM())) returns the sum of all entries.
Example: @NUM(@SUM(@NUM([ITEM_QUANTITY]*[ITEM_PRICE])))
This returns the sum of all lines L1(Qty*Price)+L2(Qty*Price)+L3(Qty*Price)…etc.).
@REAL_ROUND(Value,DecimalPlaces)
Value: Token or hard-coded value
DecimalPlaces: Number of decimal places to be rounded.
@REAL_ROUND rounds a value to the decimal place that is defined. Results uses Banker's Rounding (rounds from .6 and up, rather than .5).
Example: @REAL_ROUND([T:ITEM_UNIT_PRICE],2)
This returns two decimal places for a unit price. If the unit price sent was 5.678, the return value would be 5.68.
@REAL_TRUNCATE(Value,DecimalPlaces)
Value: Token or hard-coded value
DecimalPlaces: Number of decimal places to be truncated
@REAL_TRUNCATE truncates a value to the decimal place that is set.
Example: @REAL_TRUNCATE([T:ITEM_UNIT_PRICE],2)
If the unit price sent was 5.678, the return value would be 5.67.
@REPLACE_STRING(String,SearchFor,ReplaceWith)
String: The token to modify/search
SearchFor: Character/value/word to find
ReplaceWith: Character/value/word to replace SearchFor value with (if found).
@REPLACE_STRING finds a character/value/word and replaces it with the desired text
Example: @REPLACE_STRING([R:1.9 Header.Bill of Lading],Z,A)
Where if the BOL is '1Z2008FQ300', the value returned would be '1A2008FQ300'.
@SIGN(Value)
@SIGN returns a + or - sign based on if the value is positive or negative.
Example: @SIGN([T:ITEM_QUANTITY])
Where if ITEM_QUANTITY was 100, then it would return a + sign.
@STRING(Value)
Value: Token or hard-coded value.
All values, including numbers and calculations, are treated as strings.
Example: @INSTR([R:2.20 PAW_Invoice.Note],TRACKING #)
Finds the first “TRACKING #” in the data and returns a character count up to that
point. If [R:2.20 PAW_Invoice.Note] is “ABC123 TRACKING #”, then the value returned
would be 17.
@STRIP_CHARS(String,CharactersToStrip)
String: The token to modify/strip from
CharactersToStrip: Characters (individual) to strip
@STRIP_CHARS removes specified characters from a token. CharactersToStrip is a list, not a single word. That is, if you enter "ABC" it will not strip ABC, but rather strip all A, B, and C letters from your incoming Token regardless of their position.
Note that the ‘ character needs to be used to remove commas.
Example: @STRIP_CHARS([T:SHIP_TO_NAME],#A)
This strips out all '#' and 'A' characters found in the ship to name.
@SUM(Value)
@SUM totals all found entries of a Value.
Example: @SUM([ITEM_QUANTITY])
If two line items were sent on the PO of 4 and 6, the above statement would return the value of 10.
Example: @NUM(@SUM(@NUM([ITEM_QUANTITY]*[ITEM_PRICE])))
This will return the sum of all lines L1(Qty*Price)+L2(Qty*Price)+L3(Qty*Price), etc.
@SWITCH(String1,String2, String3, …)
@SWITCH looks to the first token set in the statement. If that is not present on the transaction then it will look to the next token set in the statement, and so on.
Example: @SWITCH([T:STORE_NUMBER],[T:SHIP_TO_ADDRESS_CODE])
This example first attempts to return the store number value. If the store number is not there, it will return the ship to code. It repeats for up to 5 fields until a field contains data.
@TRIM(String)
@TRIM removes all spaces in a field.
Example: @TRIM([R:3.4 Item.VendorNum])
If [R:3.4 Item.VendorNum] is ' AB CD ', then this would return 'ABCD'.
@TRIM_LEFT(String)
@TRIM_LEF removes all spaces to the left of a field.
Example: @TRIM_LEFT([R:3.4 Item.VendorNum])
Where if [R:3.4 Item.VendorNum] is ' ABCD', this would return 'ABCD'.
@TRIM_RIGHT(String)
@TRIM_RIGHT removes all spaces to the right of a field.
Example: @TRIM_RIGHT([R:3.4 Item.VendorNum])
If [R:3.4 Item.VendorNum] is 'ABCD ', then this would return 'ABCD'.
@UCC128_PARSE(String,Type)
String: Token or hard-coded value.
Type: 1 = Prefix (first 3 digits), 2 = Suffix (String without first 3 digits)
@UCC128_PARSE parses sections from the UCC128#.
Example: @UCC128_PARSE([R:1.9 Header.Bill of Lading],1)
If the BOL is 1Z2008FQ300, then this will return a value of 1Z2.
@UNESCAPE(String)
@UNESCAPE inserts a carriage return on an exported transaction. Use @UNESCAPE(/n) to input it into the field in Mapping Manager.
You must set the field in the Entities to “AllowTextFormattingCharacters”.
@UPPER_CASE(String)
@UPPER_CASE returns the data held within a token as all upper case. converts any upper-cased characters to lower case.
Example: @UPPER CASE([T:SHIP_TO_NAME])
Usage Examples
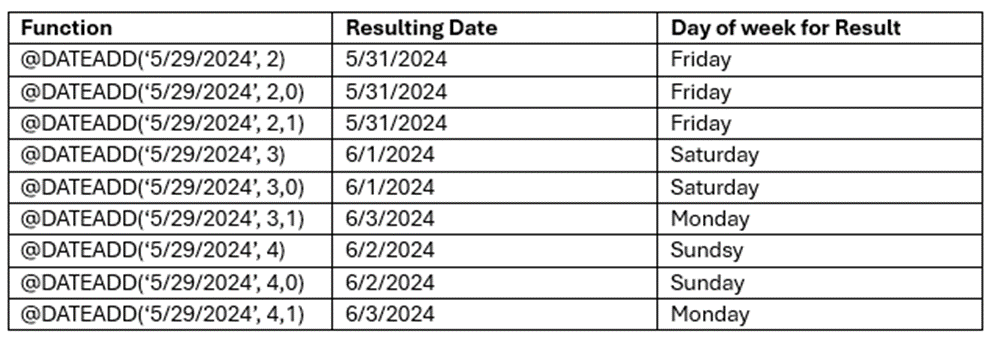
Using @DATEADD
To add 3 days to the current date: @DATEADD([T:SPECIAL_TOKEN_CURRENT_DATE],3)
To subtract 1 day from the requested delivery: @DATEADD([T:DATE_REQUESTED_DELIVERY],-1)
If 5/29/2024 is a Wednesday. Function results are as follows:
Using @NUM
Add: @NUM([T:Main.Charges.Total of Line Items]+[T:Main.Charges.Other Charges])
Subtract: @NUM([T:Items.Price]-[T:Items.Promotional Allowance])
Multiply: @NUM([T:Items.Quantity]*[T:Items.Price])
Divide: @NUM([T:Items.Quantity]/[T:Items.# Inner Pack])
Nested: @NUM([T:Items.Price]*@NUM([T:Items.Quantity]/[T:Items.# Inner Pack]))
Using @INSTR to Parse Data
The @INSTR function provides TrueCommerce users with the ability to pull multiple data elements from one field when there is a variable length.
Scenario 1
Amazon is sending the first and last name of the customer in one ship to name field which need to be separated into a first name and last name field in your TrueCommerce system.
Two questions before writing the statement: 1) What character(s) separate the values? 2) Is this character always present? If the value you are looking for via @INSTR is not always present, then an ‘if’ statement will be needed to check that the character is present.
Using 'Andrew Cutch' for this example, first and last name are separated by a single space and are always sent in this format:
First Name. This copies everything to the left of the space ...
@COPY([T:SHIP_TO_NAME],1,@INSTR([T:SHIP_TO_NAME], )-1)
... and the result is 'Andrew'.
Last Name. This copies everything to the right of the space ...
@COPY([T:SHIP_TO_NAME],@INSTR([T:SHIP_TO_NAME], )+1,255)
... and the result is 'Cutch'.
Scenario 2
Length, width, and height are kept in the same field in your TrueCommerce system. The trading partner needs to receive these as three separate values.
Two questions before writing the statement: 1) What character(s) separate the values? 2) Is this character always present? If the value you are looking for via @INSTR is not always present, then an ‘if’ statement will be needed to check that the character is present.
Using '10x11x12' for this example, values are separated by an 'x' that is always present:
Length. This copies everything to the left of the first 'x' ...
@COPY([R:1.21 Dimension],1,@INSTR([R:1.21 Dimension],x)-1)
... and the result is '10'
Width. This copies everything between the first and second 'x' ...
@COPY(@COPY([R:1.21 Dimension],@INSTR([R:1.21 Dimension],x)+1,255),1,@INSTR(@COPY([R:1.21 Dimension],@INSTR([R:1.21 Dimension],x)+1,255),x)-1)
... and the result is '11'
Height. This will copy everything after the second 'x' ...
@TRIM(@COPY(@COPY([R:1.21 Dimension],@INSTR([R:1.21 Dimension],x)+1,255),@INSTR(@COPY([R:1.21 Dimension],@INSTR([R:1.21 Dimension],x)+1,255),x)+1,255))
... and the result is '13'
Related Topics